Polar Orbiting Satellite Data Receiving and Processing
Polar-orbiting meteorological satellites such as NOAA and Metop observe the earth in sun-synchronous orbit around 850 km above its surface, providing information on variables such as atmospheric temperature and water vapor profiles. A 3-m-diameter antenna hosted on MSC’s premises to track these satellites receives observation data from them as they pass over Japan and its vicinity. The data are then processed and used for purposes such as numerical weather prediction (NWP).
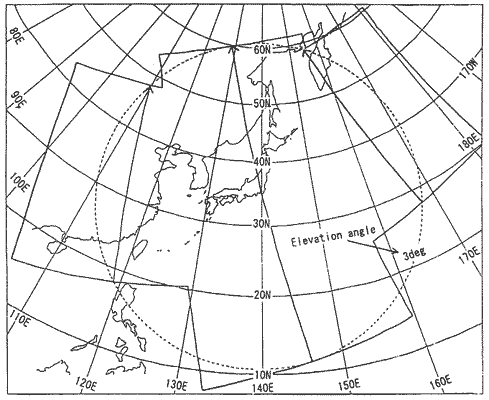
The area for data received at MSC covers a circle of about 5,500 km in diameter centered on MSC itself (shown in the figure).

DBNet
MSC also processes polar-orbiting satellite data and distributes the product to NWP users around the world through the DBNet (Direct Broadcast Network for Near-real-time Relay of Low Earth Orbit Satellite Data) framework. Further information is available on "DBNet monitoring" page.